- With the establishment of the Delhi sultanate a new ruling class emerged in India. This new class introduced a new administrative system.
- During the Sultanate period the administrative apparatus was headed by the Sultan who was helped by various nobles. There were various other offices along with the office of the Sultan. Theoretically, there was a council of Ministers Majlis-i-Khalwat to assist the Sultan.
- Sultanate administration is called as Turko-Afghan setup in Indian environment.
- The Sultans considered themselves as representatives of the Caliph.
- Iltutmish was the first sultan to receive recognition letter from Caliph.
- Delhi sultanate was neither a theocratic state nor a secular state. It was depended on ruler.
- Mullahs were interpreters of shariyath.
- Qajis were executors of Shariyath.
Territorial Administration:
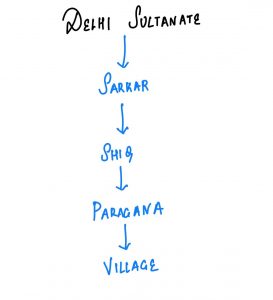
- Shiqs were controlled by shiqdar
- Paragana were controlled by amil
- Villages were controlled by village headmen.
- He is called by name muqaddam, chaudhri, khut. Patwaries were village accountant.
- The lands were classified into three categories:
Iqta land – lands assigned to officials as iqtas instead of payment for their services.
a. Khalisa land – land under the direct control of the Sultan and the revenues collected were spent for the maintenance of royal court and royal household.
b. Inam land – land assigned or granted to religious leaders or religious institutions.
